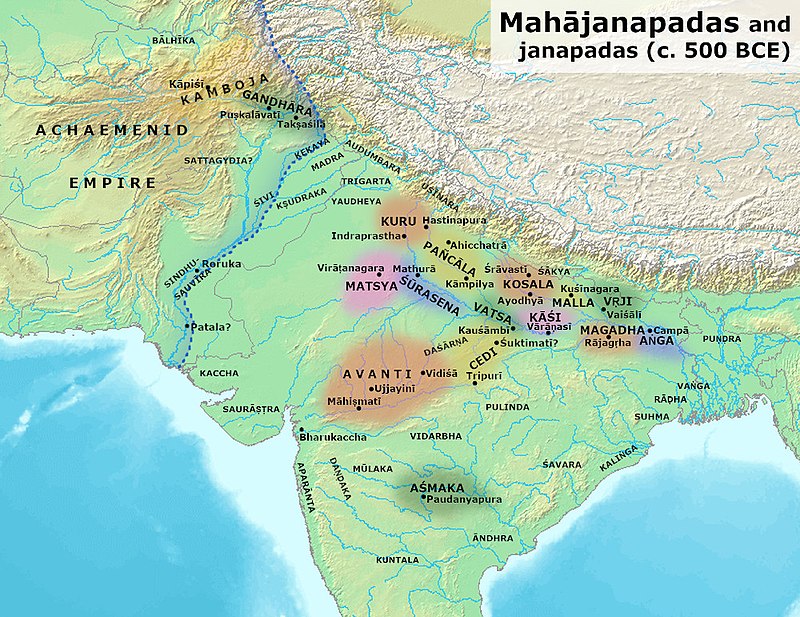
These were the sixteen kingdoms that existed in North India after series of wars and annexations. There were two types of states: Monarchical and Republican
- Malla, Vajji, Kamboja and Kuru were Republican states while Magadha, Kosala, Vatsa, Avanti, Anga, Kashi, Gandhara, Shursena, Chedi and Matsya were monarchical in nature.
- Buddhist literature like Anguttara Nikaya and Jain literature of Bhagvati Sutta gave details about these kingdoms. The most important among them was Magadha Empire and to a large part the history after later Vedic age revolve around this empire and the dynasties which ruled the region of Magadha.
- Magadha Empire was the most powerful amongst the sixteen Mahajanapadas.The empire was established by king Brihadratha.Rajgaha was the capital of Magadha but was later shifted to Pataliputra in the fourth century BCE when the ruler was Udayin considering the strategic importance of that place. The riverine route of Ganga and its tributaries made communication cheap and convenient. The large number of iron ores and its effective use made the Magadha strong. Efficient administration of ruthless and ambitious kings like Bimbisara, Ajatasattu and Mahapadma Nanda made Magadha prosperous. It was under the Haryanka Dynasty the Magadha Empire started to progress. The Haryanka Dynasty was the second dynasty to rule over Magadha after the Brihadratha dynasty. Bimbisara and Ajatasatru were the two important kings of Haryanka Dynasty. Both were the contemporaries of Lord Buddha and Mahavira. It was succeeded by the Shishunga dynasty which soon waded under the prominent Nanda Dynasty which was a turning point in the history of Magadha. Under Nandas Magadha scaled new heights.
- The Nanda Dynasty lasted from 345 BCE- 321 BCE. Mahapadma Nanda, the first king of the Nanda dynasty, added Kalinga to the Magadhan Empire. Though immensely wealthy, Harsh and inflexible taxation system, however, made the Nandas unpopular.
- It must be noted that it was during the rule of Dhan Nanda, the Alexander the Great invaded the Indian Subcontinent in 326 BC. He did not cross Beas rive and the famous Battle of Hydaspes against the valiant king Porus was his last campaign in India. Accompanied by tumultuous borders and increasing taxes, popular discontent emerged in Magadha against Nanda rule. The last Nanda king, Dhana Nanda, was overthrown by Chandragupta Maurya with the strategic brain of Kautilya who wrote Arthasastra.
- Mauryans set a new path to the Magadha empire and gave birth to some great kings of India.
