Indian Scientist, physicist, astronomer
Who is Vikram Sarabhai?
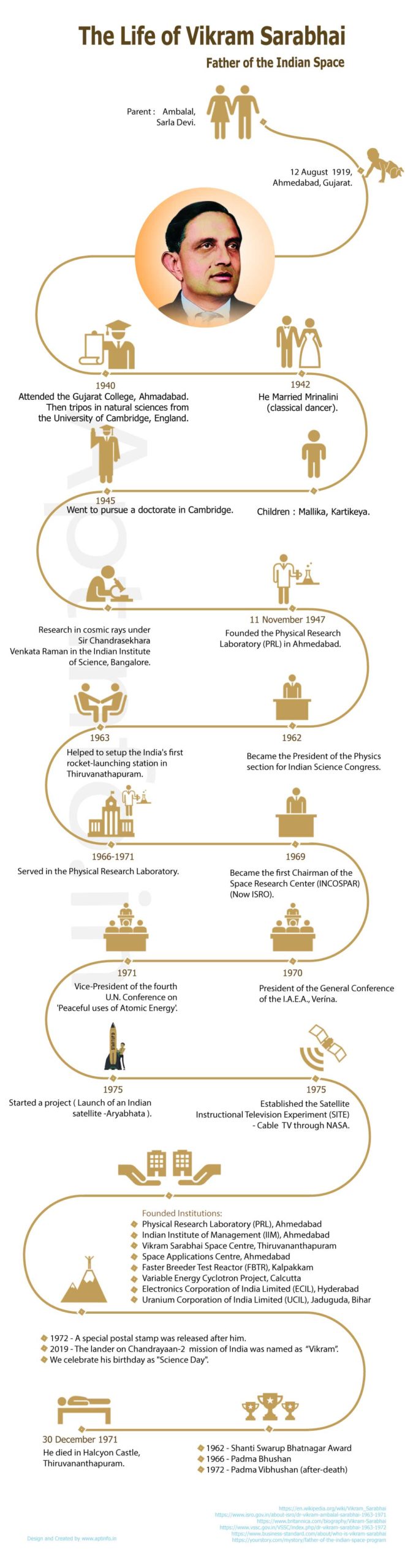
Vikram Sarabhai is an astronomer, Physicist and industrialist. He was considered as the father of Indian Space Program. He established ISRO in India. He not only initiated space research but also supported nuclear power in India. Vikram earned his doctorate from Cambridge University. While studying he was forced to return to India. And he undertook a research in cosmic rays under the guidance of Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore.
Childhood:
Vikram was born on August 12, 1919 in Ahmedabad of Gujarat, India. His parents are Ambalal and Sarla Devi. He was born to a well settled family where his father managed several textile businesses.
Personal Life:
Vikram Sarabhai had his marriage with the classical dancer Mrinalini in 1942. The couple had two children Mallika Sarabhai, Kartikeya Sarabhai. Mallika Sarabhai is an actor and an activist. His son on the other hand involved in science. He practices Jainism in his lifetime.
Career Details of Vikram Sarabhai:
On November 11, 1947 Vikram Sarabhai founded the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) in Ahmedabad. Then on 1962, he becomes the president of Physics in the Indian Science Congress. From 1966 to 1971 he served for PRL. He was the cultivator of institutions. On 1970, he becomes the President of the General Conference of the I.A.E.A., Verína. On the fourth UN conference on ‘Peaceful uses of Atomic Energy’ on 1971, Vikram acts as the vice-president. Then on 1975, started a project for the fabrication and launch of an Indian satellite. The first Indian satellite named Aryabhata was launched from Russian cosmodrome on 1975.
Vikram Sarabhai and space works:
On 1963, Vikram Sarabhai helped Homi j Bhabha to setup the India’s first rocket-launching station. The station was built in St Mary Magdalene Church near Thiruvanathapuram. The first flight was launched on 21 November 1963. It was a sodium vapour payload. On 1969, he was inaugurated as the first Chairman of the Space Research Center (INCOSPAR). Later on 1969, NASA was named as INCOSPAR. Then on 1975, he took the responsibility for bringing the cable TV facility to India. For that he got the help from Satellite instructional television Experiment (SITE).
Vikram Sarabhai awards and achievements:
- On 1962, Sarabhai got the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award.
- Then on 1966, he got the Padma Bhushan Award.
- After his death he got Padma Vibhushan Award.
- He also got the Indian Space Programmer award.
- For science and technology in physical science he got Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize.
- To honor Vikram Sarabhai, International Astronomical Union in Sydney, Australia named a crater on the moon by his name.
- The ISRO lead facility for launching vehicle which is in Thiruvananthapuram is named as The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, (VSSC) in his memory.
- Every year August 12 is observed as science day in India.
- On 1974, the International Astronomical Union at Sydney named Moon Crater BESSEL in the Sea of Serenity as Sarabhai Crater.
- On July 22, 2019, ISRO launched its first Lander and rover module to moon from India. It is sent to study the surface of moon. The Lander that carries that rover was named as Vikram in the memory of Vikram Sarabhai.
Institutions founded by Vikram Sarabhai:
- In Ahmedabad, Physical Research Laboratory (PRL).
- In Ahmedabad, Indian Institute of Management (IIM)
- In Ahmedabad, Community Science Centre
- Along with his wife, He established, Darpan Academy for Performing Arts in Ahmedabad
- In Thiruvananthapuram, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
- Next in Kalpakkam, Faster Breeder Test Reactor (FBTR).
- Then in Calcutta, Varaiable Energy Cyclotron Project
- Next in Hyderabad Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL)
- And in Jaduguda of Bihar Uranium Corporation of India Limited (UCIL)
Vikram Sarabhai death:
At the age of 52, Vikram Sarabhai died on Halcyon Castle in Thiruvananthapuram on 30 December 1971. He was found dead in his hotel room. By the time of his death he witnessed the launch of Russian rocket. And on the same day he laid foundation for the Thumba railway station.
